‘Hyperpigmentation’ is darkening of the skin. It may affect small areas of skin (small patches of skin may darken), cover larger areas of skin or affect the whole body. The condition is usually not harmful; however, it could indicate a sign of another disease.
Is it the same as pigmentation? What’s the difference?
The meaning of word ‘pigmentation’ is colouring of the skin. Disorders of skin pigmentation affect your skin colour. The colour of your skin comes from the pigment melanin.
- When your body produces excessive melanin, your skin becomes darker and it results in hyperpigmentation.
- When your body produces less melanin, your skin becomes lighter in colour and it results in hypopigmentation.
Structure of skin
The skin has three layers: Epidermis, dermis and the subcutaneous layer consisting of fat cells.
Epidermis
It is the outermost, tough and a relatively thin layer of the skin.
- Keratinocytes form the majority of the cells present in the epidermis, which originate in the basal layer or the deepest layer of the epidermis.
- Melanocytes are the cells that form the pigment melanin, which gives your skin its colour. These cells are present in the basal layer of the epidermis.
Dermis
The dermis is present beneath the epidermis. Because of its fibrous and elastic tissue, it is thicker than epidermis and this also makes the skin flexible and strong. The sebaceous glands, blood vessels, nerve endings, hair follicles and sweat glands are present in this layer of the skin.
Fatty Cells / Subcutaneous layer
This layer is present beneath the dermis. Its function is to insulate your body from heat and cold and to provide a protective padding. In addition, it stores energy in the fat cells.
Why does your skin become dark?
Sun exposure
Darkening of the skin occurs due to overproduction of melanin pigment by the melanocytes present in the skin. The major cause of skin darkening is exposure to sunlight as it triggers melanin production.
Melanin acts as skin’s natural sunblock and protects it from harmful rays of the sun. But, excessive exposure to the sun’s rays disrupt this process and it may result in dark skin or hyperpigmentation.
Skin tanning due to sun exposure occurs as a result of ultraviolet rays, also known as UV rays.

UVA rays:
UVA rays oxidize the already present pigment melanin in the skin cells and lead to quick darkening of the colour of the skin. They also release the stored melanin from the melanocytes; but, the total amount of melanin remains unaffected.
UVB rays:
Exposure to UVB rays results in melanogenesis or increased production of melanin pigment. Due to melanogenesis, there is delayed darkening of the skin, which is visible, two to three days after exposure to UVB rays.
Other factors
Your skin may become dark due to various other factors such as:
- Hormonal changes
- Increasing age
- Taking certain medicines
- After an injury or inflammation
- After an illness.
What are the causes and types of hyperpigmentation?
Depending on the causes, there are several types of hyperpigmentation.
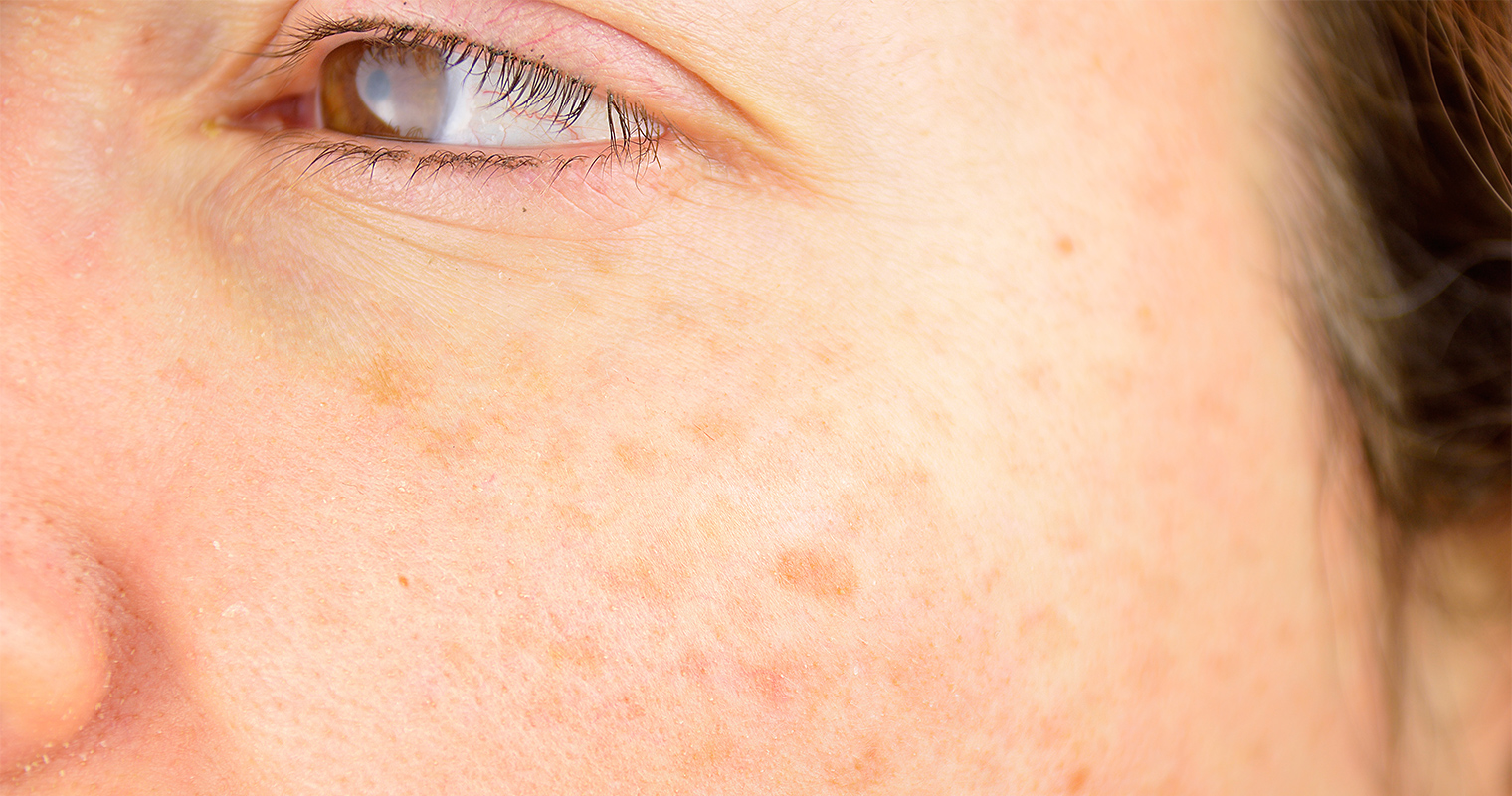
1. Sunspots/ age spots/ solar lentigines
Also known as liver spots, they are commonly present in white people who are greater than 40 years of age. They are usually harmless. You can prevent their development by avoiding exposure to the sun and wearing sunblock.
Causes and risk factors of sunspots
UV rays
Exposure to the sun (UV rays) is the main cause of development of sunspots or age spots. It was previously mentioned that ultraviolet rays’ triggers melanin production resulting in darkening of the skin. After several years of UV light exposure, production of melanin occurs in excessive amounts and it gets build up in some areas of the skin. This leads to the development of age spots.
Tanning beds
Exposure to UV rays from tanning beds may also lead to the development of age spots. Aging process, regardless of exposure to UV rays, also increases melanin production and results in the development of age spots.
Some persons are more prone to develop age spots due to genetics. For instance, people with blonde hair and fair skin are at higher risk of developing age spots.
Signs and symptoms
They are flat and oval areas of pale brown or dark brown pigmented spots on the skin. Hence, these spots are darker in appearance in comparison to the surrounding skin. They are commonly present on areas that are regularly exposed to the sun’s rays such as the face, arms, hands, shoulders, tops of feet and upper back.
Conditions that may resemble solar lentiginosis
Sunspots are harmless. There are certain skin conditions, which are more serious and may resemble sunspots. Some of these are:
- Moles
- Keratosis, a noncancerous growth of skin
- Melanoma, a type of skin cancer
- Lentigo maligna, a type of skin cancer
Visit your dermatologist if you see any of the below-mentioned characteristics in the skin spots:
- Symptoms of itching, bleeding, redness or tenderness
- A variety of colours
- Irregular edges
- Very dark-coloured pigmentation
- Increase in size of the spot over a short duration
Diagnosing sunspots
A dermatologist will inspect your skin to diagnose sunspots and to identify whether any other condition of the skin is present or not. Usually, sunspots are diagnosed by their appearance.
In case your dermatologist believes that the cause of the spot present on your skin may be different than that of a sunspot, he may order a biopsy of the skin. In this test, they remove a small portion of your skin under local anaesthesia for testing in the laboratory.
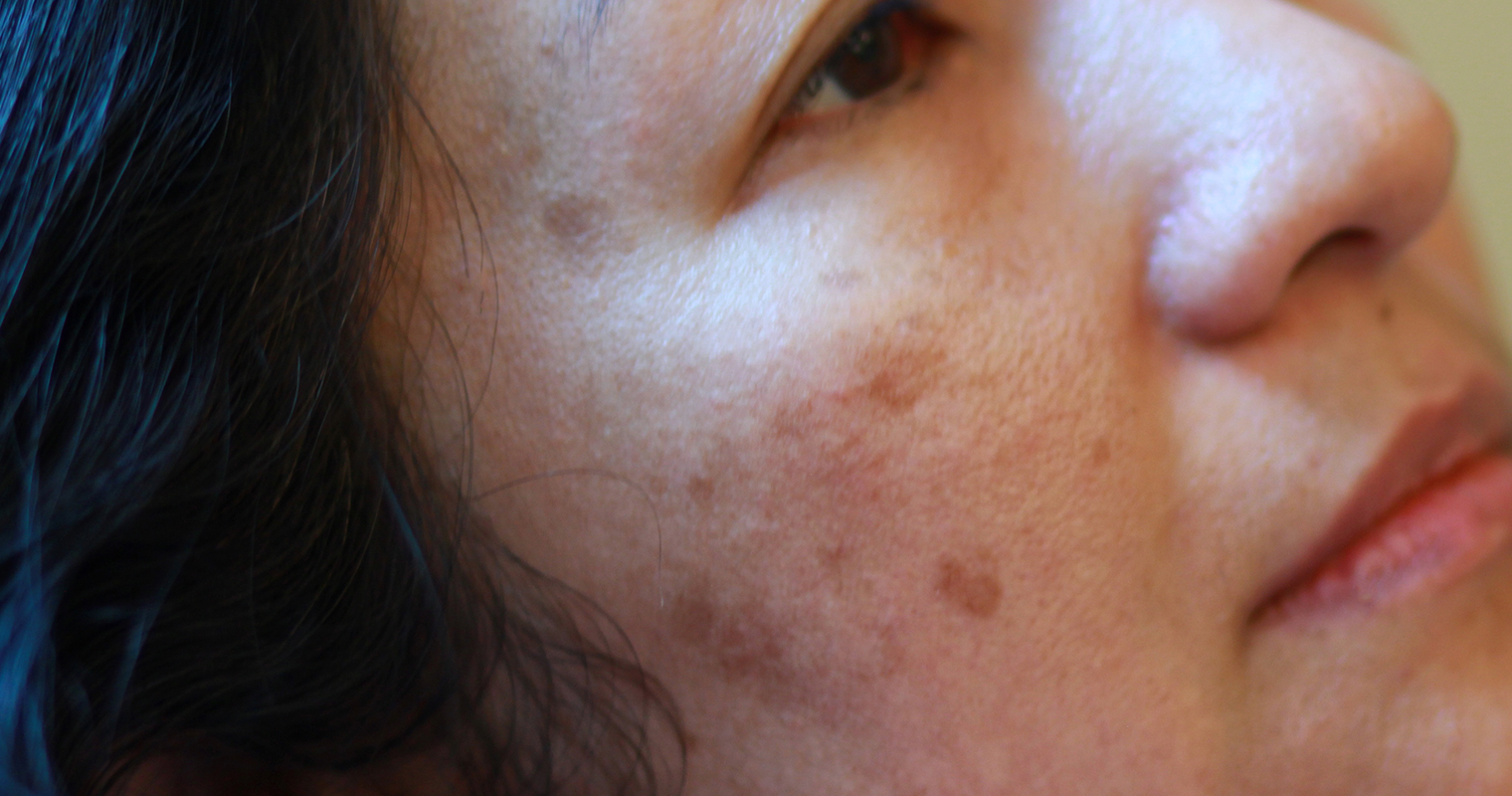
2. Melasma
Melasma is a common problem that causes discoloured and dark patches on the skin. It is called ‘mask of pregnancy’ or chloasma when it develops in pregnant females.
Signs and symptoms of melasma
Melasma causes hyperpigmented patches on your skin. It is symmetrical and usually occurs on the face. Typically, dark patches of similar types are present on both the sides of your face.
Melasma may also develop on other regions of the body, which are frequently exposed to rays of the sun. Brown coloured patches of melasma appear on:
- Cheeks
- Chin
- Forehead
- Bridge of nose
It may also appear on forearms and the neck. The discolouration of the skin is harmless; but, you may become self-conscious of the way the patches look.
Risk factors and causes of melasma
Genetics
The cause of melasma is not very clearly known; however, genetics plays a role in the development of melasma. According to a study, 40% of patients suffering from melasma had a relative with melasma. People with dark skin are more prone to develop melasma as compared to those with fair skin.
Hormonal
Sensitivity to the hormones progesterone and estrogen is also associated with the development of melasma, hence, pregnancy, hormone therapy and taking birth control pills can become triggers. Likewise, thyroid disease and stress can also result in the occurrence of melasma.
Sun exposure
Exposure to sun’s rays can result in melasma as ultraviolet rays trigger the production of the pigment melanin in melanocytes.
Diagnosing melasma
It is enough to examine the affected area for diagnosing melasma. Your dermatologist may perform certain tests to identify certain other conditions.
One such test is Wood’s lamp exam. In this test, the dermatologist holds a special type of light against your skin that allows them to look for fungal and bacterial infections. It also helps them to determine the number of skin layers affected by melasma. They may also order a skin biopsy if they suspect any serious condition of the skin.
3. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH)
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation or PIH is temporary hyperpigmentation that occurs either:
- following an injury to the skin such as a thermal burn or surgery or incorrect use of lasers, chemical peels or microdermabrasion.
- or following an inflammatory skin disorder such as acne, lichen planus, eczema and allergic reactions.
Severe trauma to the skin and inflammation of the skin disrupt the basal layer of the epidermis (for example in lichen planus). This causes the melanin present in melanocytes to leak and trap into the dermis resulting in deeper and treatment-resistant hyperpigmentation.
Inflammation of the skin also triggers the production of melanin in the melanocytes, which is then transferred to the surrounding keratinocytes.
Exposure to ultraviolet rays and certain medicines such as chemotherapeutic drugs, antimalarials drugs and tetracycline antibiotics may make the hyperpigmentation worse.
Signs and symptoms of PIH
Patches of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation are present at the region of the body with injury or the original disease, and they appear after the injury or the disease has healed. The patches appear as flat and range in colour from light brown, tan to black, and may become dark on exposure to ultraviolet rays of the sun.
Diagnosing PIH
Your dermatologist will look into your history and conduct a physical examination of the skin to diagnose the condition. They may do a skin biopsy in some cases to rule out other conditions similar in appearance to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Skin conditions that may appear like PIH include lichen planus, amyloidosis, melasma, mycosis fungoides (hyperpigmented) and pityriasis versicolor (hyperpigmented). Additionally, your dermatologist may use a Wood’s lamp exam to determine the number of layers affected by the hyperpigmentation.
Risk factors of PIH
Post-inflammatory inflammation may occur in any individual, but persons who have a dark skin colour are more prone to develop PIH. In them, the colour of PIH tends to be darker and persist for longer duration in comparison to persons with light skin colour. Pigmentation also tends to be darker in skin conditions induced by sun such as phytophotodermatitis (a condition in which inflammatory rash occurs on a sunny day after coming in contact with a plant to which you are allergic to).
You are more prone to develop PIH if you have any condition of the skin including acne, psoriasis or eczema or you have excessive exposure to UV rays.
Other diseases associated with hyperpigmentation
Apart from the three types of hyperpigmentation described above, there are many diseases which have hyperpigmentation of skin as one of the symptoms. Some of these are:
Allergic contact dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis is the occurrence of red, itchy skin after getting in contact with a substance to which you have an allergy.

Some substances, which may cause allergic contact dermatitis are:
- antibiotics
- poison ivy
- poison oak
- nickel and other metals
- sunscreens
- black henna (used in tattoos)
- rubber products (for example latex)
- preservatives such as sulfites and formaldehyde.
The allergic rash may result in hyperpigmentation of the skin upon healing.
Stasis dermatitis
It is the inflammation of the skin, which occurs in people who have poor circulation, and usually occurs in lower limbs as the blood typically pools or collects there. Skin discolouration or hyperpigmentation of the lower legs is one of the symptoms of stasis dermatitis.
Tinea versicolor
Tinea Versicolor is a condition that develops when there is a rapid growth of the fungus Malassezia on the skin surface. This results in discolored skin patches, which may occur on the chest, arms, back or neck. The patches of tinea versicolor are usually hypopigmented (lighter in comparison to the surrounding skin); but, in some people, hyperpigmented patches also develop.
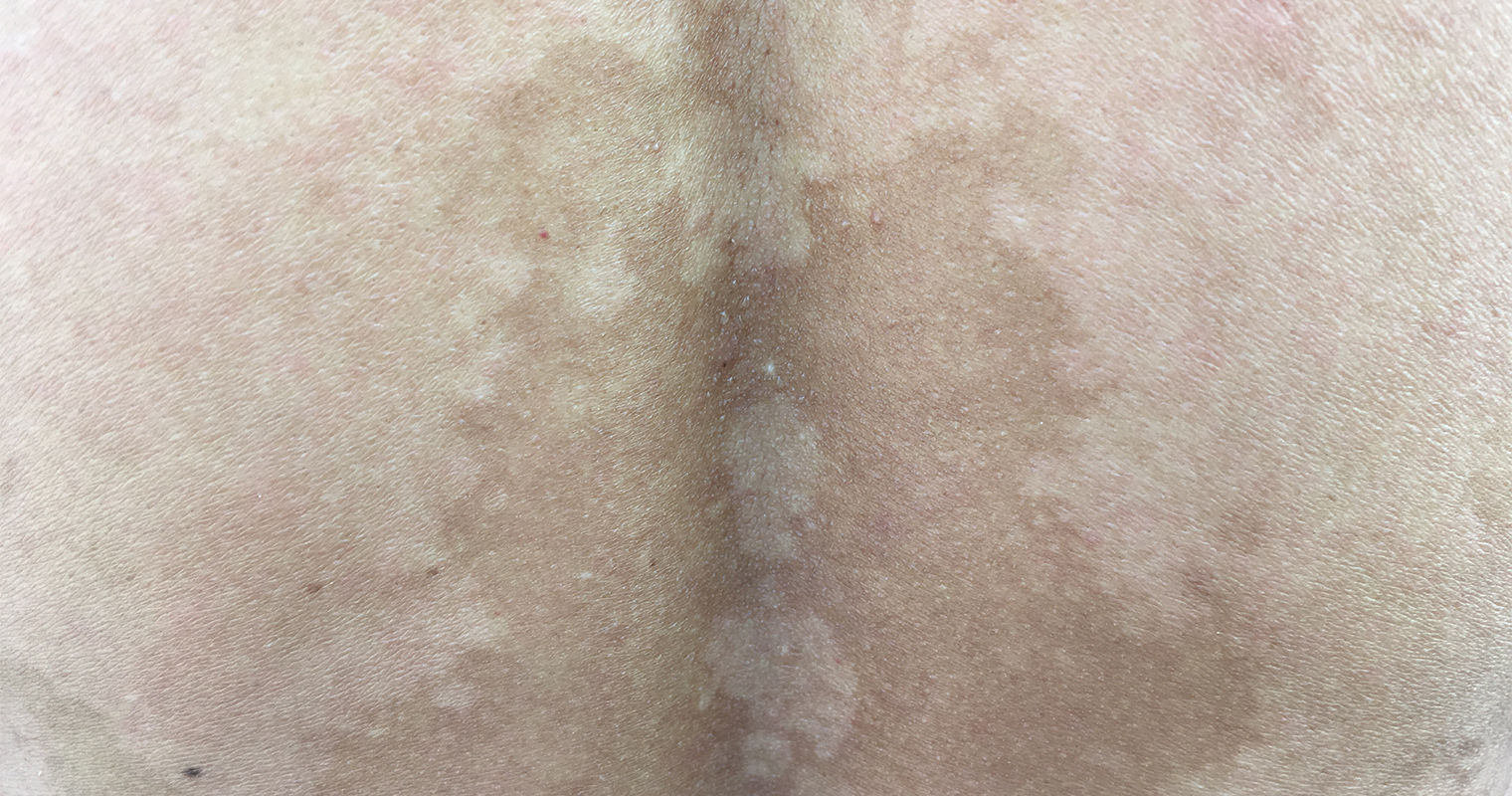
Addison’s disease
In Addison’s Disease, there is damage of adrenal glands (adrenal cortex) due to which they are unable to produce enough of aldosterone and cortisol (the steroid hormones).
Cortisol
The function of cortisol is to regulate the reaction of the body to stress and stressful situations.
Aldosterone
The function of aldosterone is to help with regulation of potassium and sodium. The adrenal cortex produces androgens or the sex hormones too.
Darkening of skin colour or hyperpigmentation is one of the symptoms of Addison’s disease apart from fatigue, weight loss, nausea, low levels of blood sugar, weakness in muscles, depression, fainting spells, etc.
Alcohol-related liver disease or ARLD occurs due to damage to your liver from many years of drinking excessive alcohol. Alcohol abuse of many years can result in swelling and inflammation of the liver. Due to this damage scarring of the liver may occur, which is also referred to as cirrhosis of the liver.
Lightening or darkening of the skin (hyperpigmentation) is one of the symptoms of alcohol-related liver disease apart from abdominal discomfort, nausea, jaundice, fatigue, loss of appetite, increased thirst, weight loss, confusion, fainting, etc.
Acanthosis nigricans
It is a common disorder of skin pigmentation. The most common sign of this condition is an occurrence of dark patches on the skin that has a velvety and thick texture and may appear on armpits, groin, elbows, neck, knuckles, knees, palms, soles of feet and lips.
It is commonly present in people who are obese or overweight, has prediabetes or diabetes and has dark skin. Ordinarily, the trigger factor for the development of acanthosis nigricans is the presence of excessive insulin hormone in your blood.
Medullary cystic kidney disease
It is a rare disease of the kidneys in which there is a formation of small sacs filled with fluid (cysts) in the medulla (center) of kidneys. As the disease progresses, scarring occurs in kidney tubules resulting in kidney failure. Kidney failure may cause symptoms of skin colour changes that may range from yellow to brown.

Ichthyosis vulgaris
It is an acquired or inherited condition of the skin, which occurs due to an inability of the skin to shed its dead cells. This results in accumulation of dead, dry skin cells in patches on skin’s surface. The condition is also referred to as ‘fish scale disease’ due to the resemblance of dead skin to fish’s scales. Typically, these scales may appear grey or brown, and most often appear on shins in dark, thick segments.
Chronic kidney disease
The irreversible and progressive destruction of kidneys is referred to as chronic kidney disease, and the two of the most common reasons for chronic kidney disease are diabetes and high blood pressure. Some other causes are autoimmune diseases like lupus or hereditary diseases like polycystic disease. The abnormally light or dark colour of skin (hyperpigmentation) is one of the various symptoms of chronic kidney disease.
Adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD)
ALD refers to different hereditary conditions, which affect the adrenal glands and the nervous system. The three main types are adrenomyelopathy, Addison’s disease and childhood cerebral ALD.
Hyperpigmentation is a symptom of Addison’s disease-the type of ALD in which the adrenal glands of the patient don’t make sufficient hormones. It is also referred to as adrenal insufficiency.
Other factors that may cause hyperpigmentation
Certain jobs or occupation may also cause hyperpigmentation as they increase your risk of exposure to sun or chemicals. Individuals who are more at risk of getting hyperpigmentation include tar or pitch workers, gardeners and those persons who work in bakeries or perfumeries.
Residual hyperpigmentation may occur due to photo-contact dermatitis, which usually occurs by using henna dyes or by tattooing.
Developing hyperpigmentation
Why is hyperpigmentation more obvious among older people?
As you age, the epidermis or the outer layer of the skin thins, though the total number of skin cells remains unchanged. The total number of melanocytes (cells that produce the pigment melanin) reduces. The cellular size of the melanocytes increases. Due to this, the skin of an aged person has less protection from harmful ultraviolet rays of the sun.
Long-standing sun exposure
Formation of age spots or sunspots is due to increased melanin production, which occurs due to more years of exposure to ultraviolet rays of the sun. Therefore, the number of sunspots or age spots tend to increase as you grow older.
Induced by medications
Use of medicines may result in skin pigmentation changes, and most of these changes occur in areas that have excessive exposure to the sun. Many types of medicines may cause hyperpigmentation including amiodarone, antimalarials, phenothiazines, clofazimine, tetracycline, minocycline, imipramine, psychotropic drugs and cytotoxic drugs.

Hyperpigmentation due to drugs may occur either because of the accumulation of melanin or accumulation of the drug, or accumulation of drug-melanin complex.
Hyperpigmentation induced by medicines is more common in older people as they consume more medicines in comparison to young people and their exposure to causal medicine is more due to the prolonged duration of consumption.
Hormonal changes
Hormonal changes, which occur during various phases of life such as during menopause or pregnancy in a female, may also cause over-stimulation of melanocytes resulting in more production of melanin. Likewise, taking birth control pills have a similar reaction in females.
Aging Process
The ability of the skin to repair and fix itself decreases with age so the damage of many years is visible. Several environmental factors apart from exposure to the sun such as smoking and habitual muscular movements can also cause uneven skin tone. Harsh treatments such as dermabrasion or exfoliation can also cause hyperpigmentation on the skin as you get older.

What types of skin are more prone to develop hyperpigmentation?
Ethnic groups who have dark skin are more prone to develop melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, whereas sunspots or age spots are more commonly present in persons with light to medium skin colour.
Similarly, people who have acne-prone skin are also more prone to develop hyperpigmentation as acne may lead to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.

What types of lifestyle are most prone to develop hyperpigmentation?
The following types of lifestyle are more prone to develop hyperpigmentation:
- Having excessive exposure to the ultraviolet rays of the sun, this may vary according to your physical activity, occupation and environment.
- Living in an environment with high air pollution levels makes you more prone to develop hyperpigmentation.
- Not using enough sun protection such as wearing sunblock or using an umbrella, wearing sun protective clothing etc.
- Suffering from anxiety and using antidepressants and drugs to treat anxiety increase the risk of developing melasma.
- Using oral contraceptives and hormonal therapy (progesterone) in menopausal females also increase the risk of developing melasma.
- Undergoing skincare treatments like Microdermabrasion or dermabrasion may also induce hyperpigmentation.
- Damaging your skin by waxing, shaving, picking at acne and blemishes, getting tattoos, etc.
Will a type of diet affect the chances of developing hyperpigmentation?
The type of diet you eat plays a vital role in the development of hyperpigmentation. According to a study published in the ‘British Medical Journal,’ hyperpigmentation of skin is an indication of a deficiency of Vitamin B12. That is to say, certain diets including a vegetarian diet may result in the deficiency of this vitamin.

Moreover, the risk of development of hyperpigmentation increases by consuming a poor diet that is high in sugar, inflammatory foods, refined grains, chemical additives and sodium.
Treatment of hyperpigmentation
There are a variety of treatment options available for hyperpigmentation, and some examples are:
Lightening creams
These are available as over-the-counter creams that help to reduce hyperpigmentation, though the stronger ones are available in prescription forms. You have to apply them once or twice a day to notice the skin lightening effects. Likewise, these topical lightening treatments are also available in gel form.
The common ingredients that are present in OTC skin lightening creams are:
- Liquorice extract
- Hydroquinone
- Niacinamide (Vitamin B3)
- N-acetyl glucosamine
Who should use lightening creams?
Lightening creams are best suited to treat flat spots like age spots or melasma, and they effectively treat hyperpigmented patches of people with all skin types. OTC creams are gels are more affordable and accessible treatments for hyperpigmentation; however, they may take a longer time to treat the affected area in comparison to professional treatments.
You should use caution while buying OTC lightening products as these may contain mercury in trace amounts.
Face acids
Face acids, also known as skin acids do their work by shedding or exfoliating the outermost skin layer. When you exfoliate the skin, a new layer of skin cells takes the place of old one. During this process, your skin colour becomes even and smooth.

Many types of face acids or skin acids are available over-the-counter at drugstores and beauty stores, and some of the popular options include:
- Alpha hydroxy acids like glycolic, citric, lactic, tartaric or malic acid
- Azelaic acid
- Salicylic acid
- Kojic acid
- Vitamin C (available as L-ascorbic acid)
Who should use face acids?
They work best for mild cases of hyperpigmentation especially on people who have fair skin colour.
Retinoids
Retinoids are Vitamin A derivatives and they are among the oldest ingredients used in over-the-counter skincare products. They can penetrate into the deeper skin layers and treat them because of their tiny molecular structure.. Generally, they are available either as OTC product or as a prescription formula.
OTC versions are weaker. In case you don’t notice any results post-treatment for a few months, consult your dermatologist regarding prescription retinoid treatment which is available as Retin-A (tretinoin).
Who should use retinoids?
Over-the-counter retinoids are safe to use for all types of skin tone, but you must consult a dermatologist in case you have dark skin colour and plan to use them for the long term.
Chemical peel
Chemical peels use acids at a strong concentration to treat the affected skin area and decrease hyperpigmentation by removing the outer layer of skin or epidermis. Deeper versions are also available, which penetrate the dermis or middle layer of skin to provide better results.
Although you may find chemical peels over-the-counter, you can get a professional-grade chemical peel at the office of your dermatologist. These peels are stronger than OTC peels and produce quick results.
Possible side effects of both OTC and in-office peels are irritation, blistering and redness.
In case you have regular exposure to the rays of the sun, then chemical peels are not the best skin whitening treatment for you. Chemical peels make your skin more sensitive to ultraviolet rays of the sun. Hence, you should take extra care in the sun for a minimum of one week post your last treatment with chemical peel.
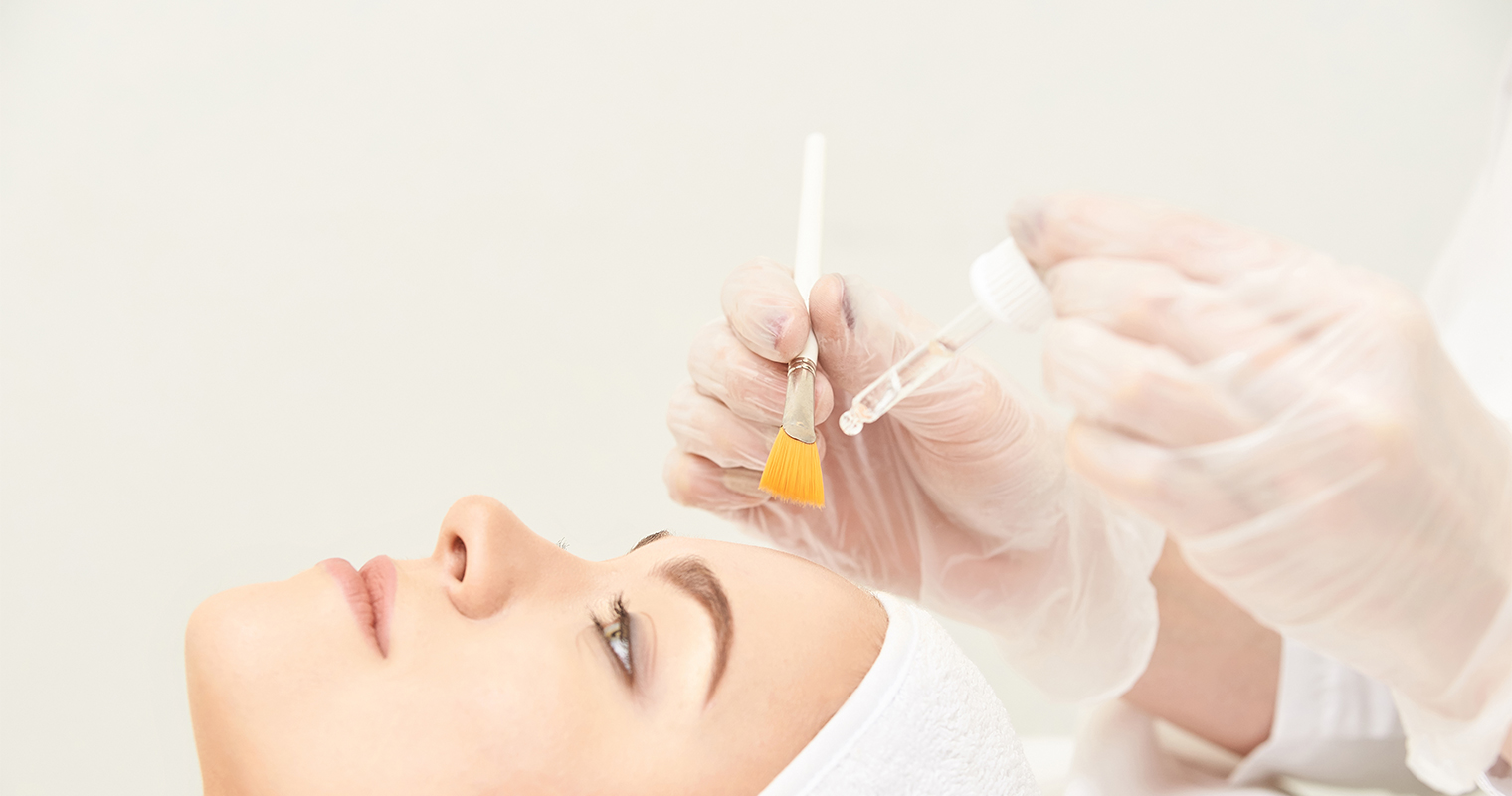
Who should use chemical peel?
Chemical peels work best for the following conditions:
- Age spots
- Melasma
- Blotchy skin
- Sun damage
They are also more effective for people who have fairer skin colour.
Skin resurfacing (Laser peel)
A laser peel treatment utilizes targeted rays of light to decrease hyperpigmentation. There are 2 kinds of lasers: non-ablative and ablative.
Ablative laser is more intense and it involves removing skin layers. For non-ablative laser procedure, the dermis is targeted to promote the growth of collagen and produce a tightening effect.
Ablative laser is stronger, but it causes more adverse effects. Both of them destroy certain skin elements to make sure that the new skin cells that grow are more toned and tighter.
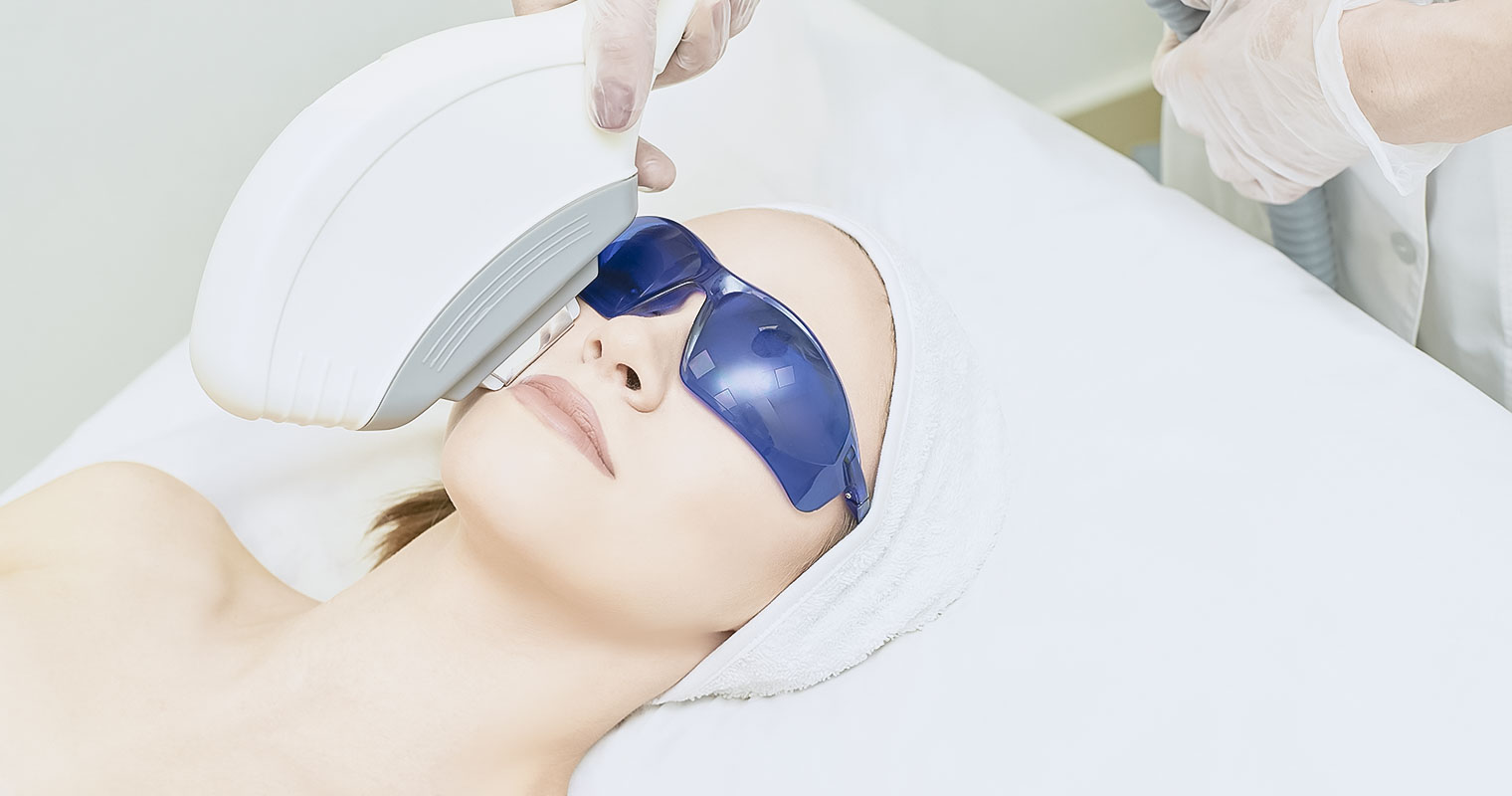
Who should use laser peel?
Ablative laser may produce better results in people who have fair skin. In some persons, non-ablative laser may produce darkening of skin instead of lightening. You should work with your dermatologist so that they can assess your extent of hyperpigmentation and skin colour and then select the right option accordingly.
IPL (Intense pulse light therapy)
IPL is a kind of non-ablative laser therapy. It is also referred to as photo facial. It stimulates the growth of collagen in the middle layer of skin (dermis). You should undergo multiple sessions to see results. IPL is utilized for general issues of hyperpigmentation; however, flat spots particularly respond well to this therapy.
Who should use IPL?
Intense pulse light therapy produces good results in people who have fair skin colour.
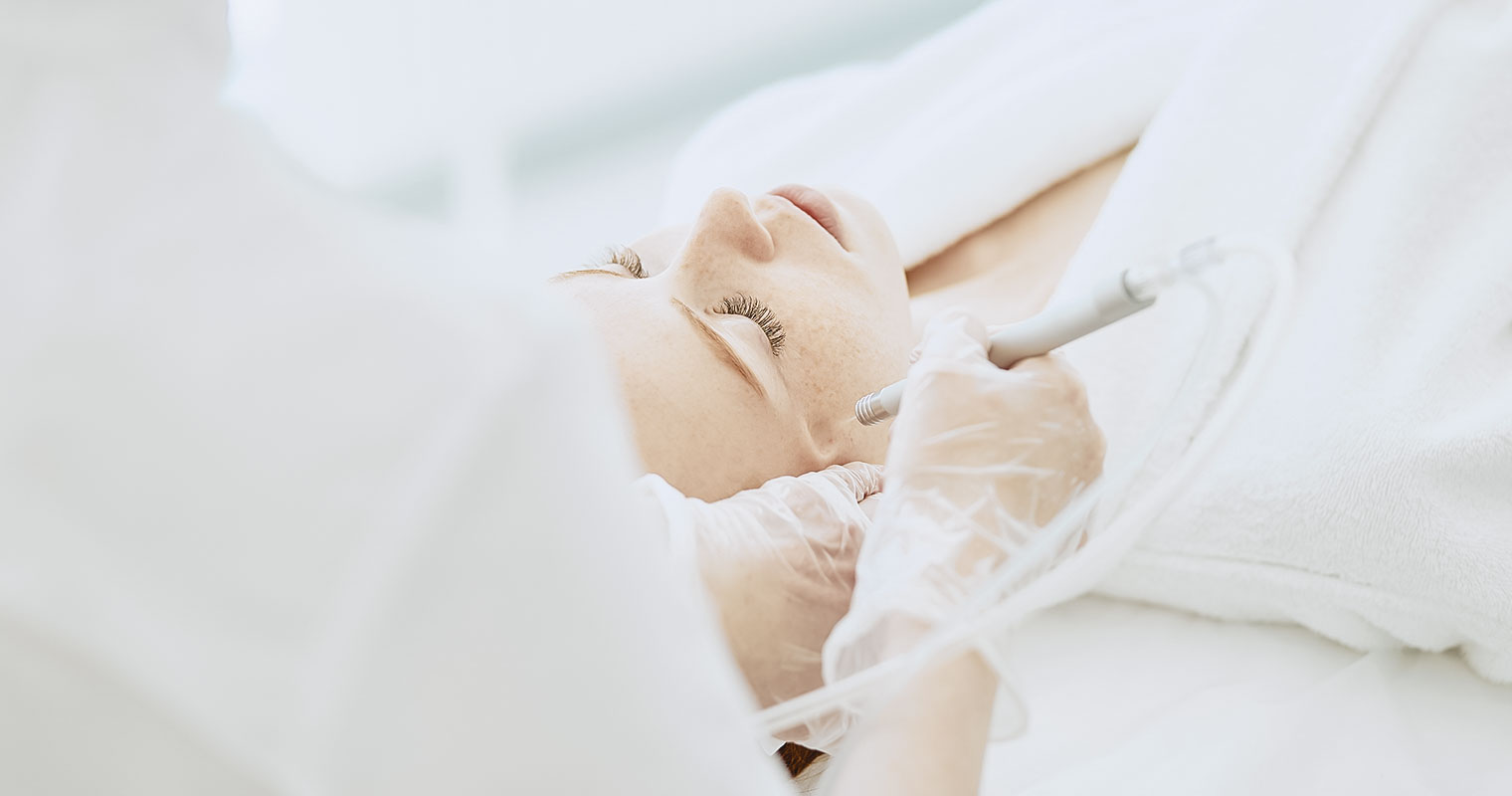
Microdermabrasion
It is an in-office procedure and is used for the treatment of hyperpigmentation, which affects the superficial layer of the skin (epidermis).
During this procedure, the dermatologist uses a hand-held device that looks like a drill and has a wire brush or any other type of abrasive attachment. This tool is swiped across the skin gently and rapidly to remove your epidermis. You may need multiple sessions of microdermabrasion to achieve good results.
Who should use microdermabrasion?
Microdermabrasion is best suited for superficial hyperpigmentation. You should work with your dermatologist to determine whether the treatment is suitable for you or not. Typically, it produces good results for people who have fairer skin.
Dermabrasion
This procedure also involves removal of the epidermis, but the effects appear down to a portion of the dermis. Though dermabrasion is used sometimes to smoothen out wrinkles, it has been used historically for treating age spots, sun damage, post-injury hyperpigmentation, etc.
Similar to Microdermabrasion, during this procedure, the dermatologist uses a handheld device that looks like a drill and has an abrasive attachment. The tool is moved across the skin gently and rapidly to remove the top portion of the dermis and entire epidermis.
Who should use dermabrasion?
Dermabrasion is a good treatment option if you want to reduce your hyperpigmentation quicker than Microdermabrasion.
It produces good results for those with fair skin, but those with a medium skin colour may develop new patches of hyperpigmentation due to this procedure.
Which skin whitening treatment is good for each skin colour?
Colour of your skin may play a vital role in the duration and intensity of hyperpigmentation treatment. Thus people who have dark skin require more time for hyperpigmentation treatments to work.
Medium skin colour may find following treatment options helpful:
- Microdermabrasion
- Chemical peels
Darker skin colour may benefit from the following treatment options:
- Kojic acid
- Glycolic acid
- OTC skin lightening creams
- Chemical peels (lower-strength)
- Laser treatments; however, when used at low intensity for a large number of sessions
- Microdermabrasion
Topical skin lightening treatments usually take a long time to produce visibly noticeable results.
Home remedies to reverse hyperpigmentation
There are many natural methods or home remedies that you can use to reverse or treat hyperpigmentation.
Lemon juice
Juice of lemon is an easily available remedy for hyperpigmentation that is also highly effective in treating hyperpigmentation spots. Lemon juice is rich in citric acid that makes it an excellent bleaching agent and is especially effective in lightening PIH (post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation).
In case you have sensitive skin, dilute the juice of a lemon before applying. Lemon juice makes the skin sensitive to the rays of the sun; hence, avoid sun exposure for some time post using lemon juice.

How to use lemon juice?
- Take juice of a fresh lemon in a bowl.
- Dip a cotton ball in the lemon juice.
- Apply the juice with the cotton ball on the affected area of the skin.
- Let it remain on the skin for about 20-30 minutes. Then rinse with water.
- Lemon juice may make the skin dry; hence, apply some moisturizer thereafter.
- Use lemon juice two times a day. You may start noticing results in your skin colour within one week of starting the treatment. Use it for a minimum of one month.
Turmeric
Turmeric is a powerful and effective remedy to treat hyperpigmentation. Its main ingredient curcumin is a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, which helps in reducing blemishes and age spots. Additionally, you may combine it with honey that helps in moisturizing and renewing damaged and dead skin.
How to use turmeric?
- Mix 1 tbsp of turmeric powder with 1 tbsp of honey in a bowl well to form a paste.
- Apply this paste on your affected skin.
- Leave the paste for about 20 minutes.
- Then rinse with lukewarm water.
- Finish by applying some moisturizer.
- Use turmeric powder and honey paste once a day for 2-3 weeks. It may take one to two months to see noticeable results depending on the amount of hyperpigmentation.
Apple cider vinegar (ACV)
Raw ACV contains acids (lactic acid, glycolic acid and citric acid) that work to lighten the skin by exfoliating it and by bleaching the dark spots present on it.

If you have sensitive skin, you should dilute the apple cider vinegar before using it on your skin. Also, it may cause a slight burning sensation, which is normal. But if the sensation of burning is excessive, wash it immediately.
How to use apple cider vinegar?
- Dilute ACV with an equal amount of water.
- Dip a ball of cotton in the mixture and apply this liquid on the hyperpigmented skin.
- Let it remain on the skin for about 20 minutes. Rinse with water.
- Repeat this treatment two times daily for six to eight weeks to reduce hyperpigmentation.
Aloe vera
Aloe Vera results in stimulation of fibroblast cells, which produce collagen. This causes regeneration of your skin. The antioxidants present in Aloe Vera protects against damage from the sun’s rays and free radicals. It also contains hormones gibberellins and auxins that help in the healing of the skin.
How to use aloe vera?
- Take a fresh leaf of Aloe Vera and scoop the gel out.
- Apply the gel on your affected skin.
- Leave it for at least half an hour. You can also leave it overnight.
- Wash with water. Use it once daily for six to eight weeks to see noticeable results.

Manuka honey
Manuka honey helps hyperpigmentation by retaining the moisture of the skin and aiding its recovery from inflammation. By releasing hydrogen peroxide, it helps in reducing the spots of hyperpigmentation and regenerating your skin.
How to use manuka honey?
- Use a cotton ball and apply fresh manuka honey to the affected regions of your skin.
- Leave it for one to two hours. Rinse it with water.
- Then apply a moisturizer.
- Use manuka honey every day and you will notice improvement within weeks. Use it until all your dark spots on the skin reduce.
Raw potato
Potatoes are rich in an enzyme referred to as catecholase that is a natural bleaching agent. Hence, raw potatoes help in reducing hyperpigmentation.

How to use raw potato?
Option 1:
- You can rub a slice of raw potato on the hyperpigmented area for one to two minutes. This transfers the potato juice to the skin.
- Leave the juice on the skin for about 10-15 minutes.
- Then rinse with water.
Option 2:
- You can also crush raw potato and take out its juice.
- Apply this juice with a cotton ball on the hyperpigmented areas.
- Leave for 10-15 minutes and then rinse with water.
- Repeat this treatment two to three times every day until the dark spots lighten.
Papaya
An enzyme known as papain is present in papaya that helps in exfoliating dead skin cells and fading dark spots.
How to use papaya?
- Mash pulp of fresh ripe papaya.
- Mix some lemon juice with it.
- Apply this mixture on the affected areas of the skin.
- Leave it on the skin for half an hour and then rinse with water.
- Results are visible after two weeks of applying papaya to your skin.
Essential Oils for Melasma and other Hyperpigmentation Treatment
The best oils for hyperpigmentation are as follows:
Melaleuca alternifolia leaf oil (Tea tree)
Tea tree oil is derived from the plant Melaleuca Alternifolia, which is a plant native to Australia. The oil is extracted from the leaves of the plant by steam distillation.
It is effective to use tea tree oil for melasma treatment because of its following properties:
- The oil is a powerful antiseptic and antimicrobial agent. It helps in fighting pimples and spots and treating symptoms and signs of inflammation.
- Helps in lightening the scars left by acne and other conditions of the skin.
- Helps in whitening the age spots and suntanned skin.
- It is a potent antioxidant and helps in removing the dead skin cells and other impurities from the skin.
Regular use of this oil significantly improves texture, general skin tone and complexion of your skin. Don’t apply this oil directly to your skin. Instead, dilute it in a carrier oil like coconut oil, olive oil or almond oil. Before using it, perform a patch test.
Coconut Oil
Coconut oil helps hyperpigmentation, especially with fading of scars caused by acne, injury and stretch marks. Here’s how it works:
- Rich in vitamin E, coconut oil acts as a thick moisturizing barrier to help the skin heal. Vitamin E is also an antioxidant that prevents oxidation and reduces pigmentation.
- It boosts collagen production which helps the new skin tissues bind together.
- It evens out the skin tone by getting rid of redness caused by inflammation.
Argania spinosa kernel oil (Argan)
Argan oil is rich in linoleic (omega 6) and oleic (omega 9) fatty acids. Both of these oils aid acne-prone skin by reducing inflammation, improving moisture levels of skin and permeability of the skin. It is also a rich source of vitamin A, vitamin E and several antioxidants.
One of the top Argan oil benefits is that it acts as a skin toner, and helps in exfoliating your skin. You can make your own exfoliation mixture as follows:
- Mix a few drops of pure Argan oil with 1 tbsp of brown sugar.
- Rub on your face or the hyperpigmented area in circular motion.
- Massage the mixture for 2-4 minutes.
- Rinse the area with lukewarm water.
- Don’t forget to moisturize after.
Regular exfoliation using Argan oil helps in removing the dead skin cells and reducing the appearance of wrinkles and dark spots, while providing you with a brighter and younger complexion. Argan oil also helps in reducing the levels of sebum in people who have oily skin. Hence, it is a good remedy for acne.
Sesamum indicum seed oil (Sesame oil)
Sesame oil is derived from Sesamum Indicum, which is a tall herb belonging to the family Pedaliaceae. Commonly utilized as an ingredient in food and as a condiment, it also has medicinal uses and is among the oldest plants in the world that are used in the form of oil. It is used since ancient times in food and medicine, and today, it forms a common ingredient of massage and skin oils, products of hair care, soaps, cosmetics, sunscreens and perfumes.
Sesame oil is rich in antioxidants – sesamol, sesamin oils and sesamolin, which:
- Help to fight free radicals and protect your skin from sun damage.
- Has great soothing, emollient and moisturizing qualities.
- Acts as a natural sunscreen.
Massaging your skin with sesame oil helps in improving blood circulation and healing your skin, as well as lightening dark spots.

Perilla ocymoides seed Oil (Perilla)
Perilla seed oil is derived from the seeds of Perilla ocymoides, which is a bushy and leafy herb from the mint family, also referred to as wild basil. This oil is a rich source of omega-3, omega-6 and omega-9 fatty acids. It has antioxidant properties; therefore, it helps to fight against free radicals and protect your skin from sun damage.
According to a study published in the ‘Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health,’ the plant extracts of Perilla markedly inhibited the activity of enzyme tyrosinase that is the main enzyme involved in melanin synthesis in mice cells. Hence, it can be applied for skin lightening purposes. The oil also has skin cleansing properties removing the impurities and dirt from the skin.
Simmondsia chinensis Seed Oil (Jojoba)
Jojoba oil is derived from the seeds of the plant Simmondsia Chinensis, a shrub that is native to northwestern Mexico, southern California and southern Arizona. Although, it is referred to as an oil, it is in fact a liquid wax of plant. It is used to treat a variety of ailments in folk medicine.
The effectiveness of jojoba oil
- Jojoba oil is used commonly to treat psoriasis, acne, chapped skin and sunburn, as it is a rich source of Vitamin E, which is a powerful antioxidant.
- It helps in protecting your skin against sun’s rays and damage caused by free radicals, and also helps in healing sunburn due to its vitamin E content.
- It also quickens the regeneration of skin cells; thus, it helps in treating scars and discolouration due to acne and also wrinkles and fine lines.
- Jojoba oil is a rich source of B complex vitamins, which are also powerful antioxidants. They help your body fight against free radicals and prevent cell damage.
- Vitamin B5 in Jojoba oil helps in speeding up healing of wounds and cuts. Besides delaying the premature aging of your skin, it also prevents the appearance of dark spots and wrinkles.
Vitis vinifera seed oil (Grape seed)
Grapeseed oil is derived from grape seeds after the wine is made from them. It is odourless and colourless with a yellowish/greenish tint and has a light and thin consistency that is lighter than jojoba and coconut oils. Also, it is rich in essential fatty acids such as linoleic acid, Vitamin E and Vitamin C and flavonoids.
Due to its Vitamin E and Vitamin C content, it has excellent skin lightening and brightening properties as both these vitamins help in improving skin colour and also lightens it. In case you have blemishes, hyperpigmentation or scars, then apply this oil to your skin and you can notice the results within some time.

Oenothera biennis oil (Evening primrose)
Evening primrose oil is derived from the seeds of Oenothera Biennis plant. It is native to Europe and North America, and is great for the general health of your skin. It helps in lightening the skin and reducing hyperpigmentation and dark spots.

Helianthus annuus seed oil (Sunflower)
Sunflower oil is derived from the seeds of plant Helianthus Annuus. It is a rich source of essential fatty acids and vitamin E. The latter has antioxidant properties that help in regenerating the damaged skin cells and protect them from harsh ultraviolet rays of the sun.
Sunflower seed oil also exhibits anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits due to its high flavonoids content and helps in brightening skin tone.
Corylus americana seed oil (Hazelnut)
Hazelnut oil is extracted from the seeds of Corylus Americana plant. It is rich in essential fatty acids and vitamins that help in protecting your skin against damage from the sun, boosting production of collagen and more.
The vitamin E present in hazelnut oil helps in protecting your skin by fighting against free radicals and preventing sun damage. According to a study published in the ‘Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery,’ vitamin E present in hazelnut oil also helps in reducing hyperpigmentation.
Prunus amygdalus dulcis oil (Sweet almond)
Almond oil is derived from the nutrition-enriched almonds and it has incredible benefits for your skin. It is a rich source of vitamin E, which helps in reducing hyperpigmentation.
Sweet almond oil also helps in protecting your skin against the damaging UV rays. According to a study published in the ‘Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology’ topical application of almond oil prevents the structural damage caused by ultraviolet radiation and also decelerates the process of photoaging.

Persea gratissima oil (Avocado)
Avocado oil is derived from the fresh fruit of the Persea Gratissima plant. Avocado oil is rich in:
- Vitamins A, B, C, D, E, and K
- Phytosterols
- Omega-9 fatty acids
- Lecithin
- Beta-carotene
- Sterolins
All these active ingredients promote skin regeneration and healing and protect the skin from the aging effects of pollution and ultraviolet rays of the sun.
Avocado oil can penetrate into the deep layers of the skin and deliver excellent results. The sterolins present in avocado oil help in rejuvenating and treating skin damaged from sun and lightening the hyperpigmented areas of skin. At the same time, they also help in lightening the blemishes present on the skin. The various vitamins present in avocado oil fight the free radicals and improve skin discolouration, whether it is from sun damage or scar.
Rosa damascena flower oil (Damask rose)
Rose essential oil is derived from the steam distillation of petals of roses. It is among the most expensive essential oils as it takes about 22 lbs of rose petals to make a five ml bottle of rose essential oil.

The ingredients present in rose oil are citronellol, geraniol, nonadecane, nerol, linalool, heneicosane, quercetin and kaempferol, which contribute to the following effects:
- Antioxidant effects, due to which it helps in reducing the formation of wrinkles, discolouration of the skin and fine lines.
- Helps in skin lightening and promoting an even tone of skin and a healthy complexion.
Santalum album oil (Sandalwood)
Sandalwood oil is an essential oil that is derived by steam distillation of the chips of the heartwood of Santalum Album (Sandalwood) tree. The main components of sandalwood oil are beta-santalol and alpha-santalol.
How sandalwood oil works
- Fights the free radicals and reduces aging of the skin due to its antioxidant active ingredients.
- Has antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties; therefore, it helps to reduce inflammation associated with acne.
- Helps in lightening your skin and smoothening skin discolourations.
- Breaks down the excess melanin pigment in your skin, resulting in an even skin colour.
Because sandalwood is so useful and effective, its limited source drives the prices high. Find out more about its environmental issues and how countries are dealing with its impact.
Boswellia carterii oil (Boswellia), a.k.a. Frankincense
It is derived from frankincense resin that is burned in homes of Arabs as incense since ancient times.
Effectiveness of Boswellia
- Has potent healing and antiseptic properties.
- Possesses effective scar healing properties.
- It is also good at reducing hyperpigmentation patches on the skin.
You should mix it with a carrier oil to remove dark spots and brighten your complexion. You may also mix Frankincense essential oil with shea butter as it blends well with shea butter.
Rosa canina fruit oil (Rosehip)
Rosehip oil is derived from the seeds and fruits of the rose plant. Its active ingredients include:
- Essential fatty acids
- Vitamins A, C and E
- Beta-carotene & lycopene
How do these active ingredients work
- All these vitamins collectively help in protecting against damage caused by sun and prevent photoaging.
- Essential fatty acids and vitamins help in nourishing your skin.
- Vitamin A & C helps in exfoliating and brightening your skin
- As an antioxidant, Vitamin E helps in fighting against free radical damage and reduces inflammation.
- Vitamin A & E in rosehip oil is effective against hyperpigmentation
- Vitamin A contains ingredients such as retinoids, which are well known for their skin whitening ability.
- Beta-carotene and lycopene have skin-lightening effects, hence, rosehip oil is frequently used in natural and organic skin lightening products.
Vaccinium macrocarpon seed oil (Cranberry)
Cranberry seed oil is an essential oil derived from the seeds of cranberry. Cranberries are famous for their variety of health benefits. Due to their high levels of antioxidants and nutrients, they are considered as one of the superfoods.
While cranberries are consumed widely in the form of smoothies and juices, cranberry oil also provides excellent benefits when it is applied topically. Because it is rich in antioxidants, phytosterols and essential fatty acids, it has natural properties to protect against sun damage and also makes it capable to fight damaging free radicals.
Cranberry oil also contains tocotrienol that is a rare type of vitamin E and a carotenoid (a precursor of vitamin A), both of which helps in skin whitening.
Linum usitatissimum seed oil (Linseed oil)
Linum usitatissimum oil is oil obtained from flax seeds. The use of flaxseed oil in skincare is prevalent since ancient times. Usually, it is used in the treatment of a variety of skin problems including acne, Rosacea, sunburn and psoriasis.
This oil is used in many natural sunscreen creams and lotions that help in protecting the skin from the harmful rays of the sun. Flaxseed oil is a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids that are excellent for the health of skin and provides it anti-inflammatory properties.
Lavandula angustifolia oil (Lavender)
Lavender is an essential oil that is prepared by steam distillation of the flowers of the lavender plant. Lavender oil is very gentle and potent essential oil. However, it may irritate sensitive skin when applied directly. Hence, you should apply it by mixing it with a carrier oil such as coconut oil.
How lavender oil works
- Has antimicrobial activity which prevents acne breakouts.
- Possesses anti-inflammatory properties. This helps in reducing the redness and blotching of your skin.
- Helps in reducing age spots and lightening other kinds of hyperpigmentation of the skin.
- It is also a rich source of antioxidants; therefore, it helps in protecting your skin from free radical damage. It also helps in relieving sunburns.
Camellia sinensis (Green tea)
Green tea has many benefits for the skin both in oil and powder form.
According to a study, among ten traditional Korean teas, green tea was able to inhibit most strongly the activity of tyrosinase (the enzyme involved in the production of pigment melanin). The main ingredients in green tea are ECG (epicatechin 3-O-gallate), GCG (gallocatechin 3-O-gallate) and EGCG (epigallocatechin 3-O-gallate).

The effectiveness of green tea for hyperpigmentation
- By inhibiting the activity of enzyme tyrosinase, green tea helps in reducing hyperpigmentation.
- The active ingredients found in green tea are also important antioxidants that fight free radical damage and prevent sun damage.
- Females in China use green tea oil for many homemade beauty applications.
- When added to sunscreen, green tea improves the SPF value of a sunscreen by around 5 points.
Hydrolyzed silk
While silk is a treasured textile, attention is currently focused on utilizing extracts of silk in skincare products. Silk extracts are believed to produce better skin health and aesthetics, and is derived from the cocoon of silk caterpillar, and contains two main proteins sericin and fibroin. In skincare products, both types of silk proteins are beneficial; but sericin is most widely used because it is cheaper while offering inferior results compared to fibroin.

According to studies, silk extracts help in wound healing due to the proteins present in the extract, which have potent antioxidant and UVB rays protective properties. At the same time, they inhibit the enzyme tyrosinase; thereby, inhibiting the formation of the pigment melanin. This promotes a brighter and lighter complexion. Hence, silk extracts provide skin brightening effects with UVB rays protection.
Pearl powder
Pearl powder is made by finely milling freshwater pearls. According to studies, pearl powder increases the activity of the antioxidant enzyme SOD (super-oxide dismutase), which quickly removes pigmentation. As a result, skin is made brighter and whiter. It is able to remove melasma, age spots, dark patches and freckles from the skin, as well as protects your skin from the damaging rays of the sun.
The above listed all the natural ingredients targeting pigmentation. Below are 3 Powerful products containing these ingredients
 White Paint Soap contains Green tea, Sesame oil, Perilla, Jojoba, Grape Seed, Evening Primrose, Sunflower, Hazelnut, Sweet Almond, Avocado, Damask Rose, Rosehip, Cranberry, Linseed Oil, Hydrolyzed Silk, Pearl Powder and these are able to deal with your pigmentation effectively.
White Paint Soap contains Green tea, Sesame oil, Perilla, Jojoba, Grape Seed, Evening Primrose, Sunflower, Hazelnut, Sweet Almond, Avocado, Damask Rose, Rosehip, Cranberry, Linseed Oil, Hydrolyzed Silk, Pearl Powder and these are able to deal with your pigmentation effectively.
 Koicha Tea Soap is an upgraded verion of White Paint Soap. Although they carry almost the same ingredients, “Koi” means concentrated in Japanese. The green tea extracts used in Koicha is premium and concentrated, making it even more effective to deal with your signs of aging. (Ingredients listed above present in Koicha Tea Soap are Green Tea, Argan, Sesame Oil, Perilla, Jojoba, Grape Seed, Evening Primrose, Sunflower, Hazelnut, Sweet Almond, Avocado, Damask Rose, Tea Tree, Sandalwood, Frankincense and Hydrolyzed Silk)
Koicha Tea Soap is an upgraded verion of White Paint Soap. Although they carry almost the same ingredients, “Koi” means concentrated in Japanese. The green tea extracts used in Koicha is premium and concentrated, making it even more effective to deal with your signs of aging. (Ingredients listed above present in Koicha Tea Soap are Green Tea, Argan, Sesame Oil, Perilla, Jojoba, Grape Seed, Evening Primrose, Sunflower, Hazelnut, Sweet Almond, Avocado, Damask Rose, Tea Tree, Sandalwood, Frankincense and Hydrolyzed Silk)
 German Blue is the anti-aging serum crafted specifically for aging concerns. It include these ingredients listed above: Argan, Jojoba, Grape Seed, Evening Primrose, Sweet Almond, Tea Tree, Rosehip and Lavender. Not only is it able to handle pigmentation, it is able to moisturize dry skin and smooth out wrinkles, the two common concerns of aging skins.
German Blue is the anti-aging serum crafted specifically for aging concerns. It include these ingredients listed above: Argan, Jojoba, Grape Seed, Evening Primrose, Sweet Almond, Tea Tree, Rosehip and Lavender. Not only is it able to handle pigmentation, it is able to moisturize dry skin and smooth out wrinkles, the two common concerns of aging skins.
Other ways to prevent hyperpigmentation
The various ways to prevent hyperpigmentation are as follows:
Avoid exposure to ultraviolet rays of the sun
The foremost cause of hyperpigmentation is excessive exposure to the sun’s rays. Hence, always use a sunblock (broad-spectrum) of SPF of at least 30 or more, which contains zinc oxide or titanium dioxide. UV rays pass easily through clouds; therefore, apply sunblock even on cloudy days and during winters. It is especially important to wear sunblock during swimming and prolonged outdoor activities. You should also remember to reapply sunblock after every 2 hours to maintain its effectiveness.

Avoid excessive sun exposure
Apart from applying sunblock, use natural measures to avoid excessive sun exposure such as wearing clothing especially designed to protect from the sun. Wear clothes with good coverage so that it limits your exposure to sun’s rays. Additionally, wearing a wide-brimmed hat also helps to shade your face and ears, or using an umbrella or seeking shade under a tree. Avoid going out in the sun during peak hours (between 11 am and 4 pm) and keep a note of UV index (a measure of the strength of UVB and UVA rays of sun on a particular day). Also, avoid going out on days when the UV index is high.
Avoid waxing as a hair removal method
Avoid waxing as a hair removal method as waxing may irritate your skin and make hyperpigmentation such as melasma even worse. In case it is important for you to remove hair, discuss with your dermatologist about other safer alternatives that do not promote hyperpigmentation.
Stop using skincare products that cause irritation
Discontinue the use of topical skincare products that cause irritation. Instead use mild soaps, shower gels, lotions and other products for skincare that are non-comedogenic and gentle. Generally, anything which burns, stings or irritates the skin has the chances of making the hyperpigmentation worse.
Use organic & natural skin lightening products
If you notice dark spots on your skin, immediately start using organic skin lightening products. You should buy products that contain natural ingredients such as vitamin C, kojic acid, green tree, liquorice root etc. as they inhibit the production of melanin pigment in the skin.
Do not pick or scratch your skin
Avoid scratching and picking your skin. If you see a blackhead, insect bite or a pimple on your skin, avoid picking or scratching it as doing so increases inflammation, which can lead to hyperpigmentation.
Check your skin health regularly
Get regular checkups of your skin by a dermatologist whether you have dark spots or not. This helps in quickly curbing any darkening of skin with a prescription treatment such as hydroquinone.
Treat the problem promptly
If you are prone to develop hyperpigmentation on your skin, make sure to address other skin issues that may result in dark spots promptly. For instance, treat acne immediately with medicine. Use insect repellents to prevent bites of insects.
Be informed of medication side-effects
Keep yourself fully informed about the potential adverse effects of medicines you are consuming as one of the adverse effects may be hyperpigmentation of the skin. Alternatively, discuss with your doctor if they can prescribe any alternatives to the ones you are taking. In case you think that your melasma has occurred due to the birth control pills you are taking, discuss with your doctor and ask about alternative birth control options.
References
https://www.healthline.com/symptom/increased-skin-pigmentation
https://medlineplus.gov/skinpigmentationdisorders.html
https://www.myvmc.com/anatomy/skin-colour/
https://www.healthline.com/health/liver-spots#conditions
https://www.healthline.com/health/melasma#risk-factors-and-causes
https://www.dermnetnz.org/topics/postinflammatory-hyperpigmentation/
https://www.dermcoll.edu.au/atoz/post-inflammatory-hyperpigmentation/
https://www.healthline.com/health/stasis-dermatitis-and-ulcers#symptoms
https://www.healthline.com/health/tinea-versicolor#symptoms
https://www.healthline.com/health/addisons-disease#symptoms
https://www.healthline.com/health/alcoholism/liver-disease#types-and-symptoms
https://www.healthline.com/health/acanthosis-nigricans#risk-factors
https://www.healthline.com/health/medullary-cystic-kidney-disease#symptoms
https://www.healthline.com/health/ichthyosis-vulgaris#symptoms
https://www.healthline.com/health/chronic-kidney-disease#symptoms
https://www.healthline.com/health/adrenoleukodystrophy#types
https://www.consultant360.com/content/skin-disorders-older-adults-age-related-pigmentary-changes-0
https://blackpaint.com.sg/hyperpigmentation/
https://www.stylecraze.com/articles/pigmentation-causes-preventive-measures/#gref
https://www.jstor.org/stable/20381265?seq=1#page_scan_tab_contents
https://draxe.com/hyperpigmentation/
https://www.healthline.com/health/beauty-skin-care/hyperpigmentation-treatment#options-for-each-skin-tone
https://www.fabhow.com/get-rid-of-hyperpigmentation.html
https://india.curejoy.com/content/home-remedies-for-hyperpigmentation/
http://www.skinwhiteningscience.com/top_skin_whitening_agents_top_20_green_tea.html
https://draxe.com/argan-oil-benefits-skin-hair/
https://articles.mercola.com/herbal-oils/sesame-oil.aspx
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17454565
https://www.annmariegianni.com/perilla-seed-oil-for-sensitive-skin/
https://draxe.com/jojoba-oil/
https://beautymunsta.com/beauty-benefits-of-grapeseed-oil-for-skin-hair/
https://www.stylecraze.com/articles/benefits-of-evening-primrose-oil-for-skin-hair-and-health/#gref
https://www.cosmeticsandtoiletries.com/formulating/function/active/105876463.html
https://www.naturalfoodseries.com/13-benefits-sunflower-oil/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3663177/
https://www.healthline.com/health/beauty-skin-care/hazelnut-oil-for-skin#hyperpigmentation
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17348990
https://draxe.com/almond-oil/
https://www.sunsaferx.com/health-and-wellness/hyperpigmentation/
https://www.sunsaferx.com/health-and-wellness/melasma/
https://skindeepskinhealth.wordpress.com/2012/11/02/proving-the-amazing-benefits-of-avocado-oil/
https://www.superfoodly.com/benefits-of-rose-oil-for-skin/
http://mixedupbeauty.net/tea-tree-oil-for-skin-tags-whitening/
https://www.healthline.com/health/tea-tree-oil-for-skin#benefits-and-uses
https://thebestorganicskincare.com/sandalwood-essential-oil-5-benefits-for-a-healthy-skin/
https://beautymunsta.com/9-effective-essential-oils-for-hyperpigmentation/
https://www.ewg.org/skindeep/ingredient/717033/BOSWELLIA_CARTERI_%28FRANKINCENSE%29_OIL/#.W69XFNczbIU
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3569896/
https://www.healthline.com/health/beauty-skin-care/rosehip-oil-for-face#colorcorrecting
https://riorosa.co.uk/blogs/ingredients/cranberry-seed-oil-vaccinium-macrocarpon
https://www.cosmeticsandtoiletries.com/formulating/function/moisturizer/12597266.html
https://aryanveda.in/atsi-linum-usitatissimum/
https://www.thealternativedaily.com/benefits-of-lavender-oil-for-skin/
https://www.selfgrowth.com/articles/pearl-powder-is-the-key-to-flawless-skin-and-longevity
https://www.lneonline.com/silk-extract/









